Navigating Treatment for an Enlarged Prostate: A Comprehensive Guide
Phnom Penh, Cambodia – For men experiencing the disruptive symptoms of an enlarged prostate, medically known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a wide array of effective medical treatments are available. These options range from simple lifestyle adjustments to medications and various surgical procedures, tailored to the severity of symptoms and individual patient factors.
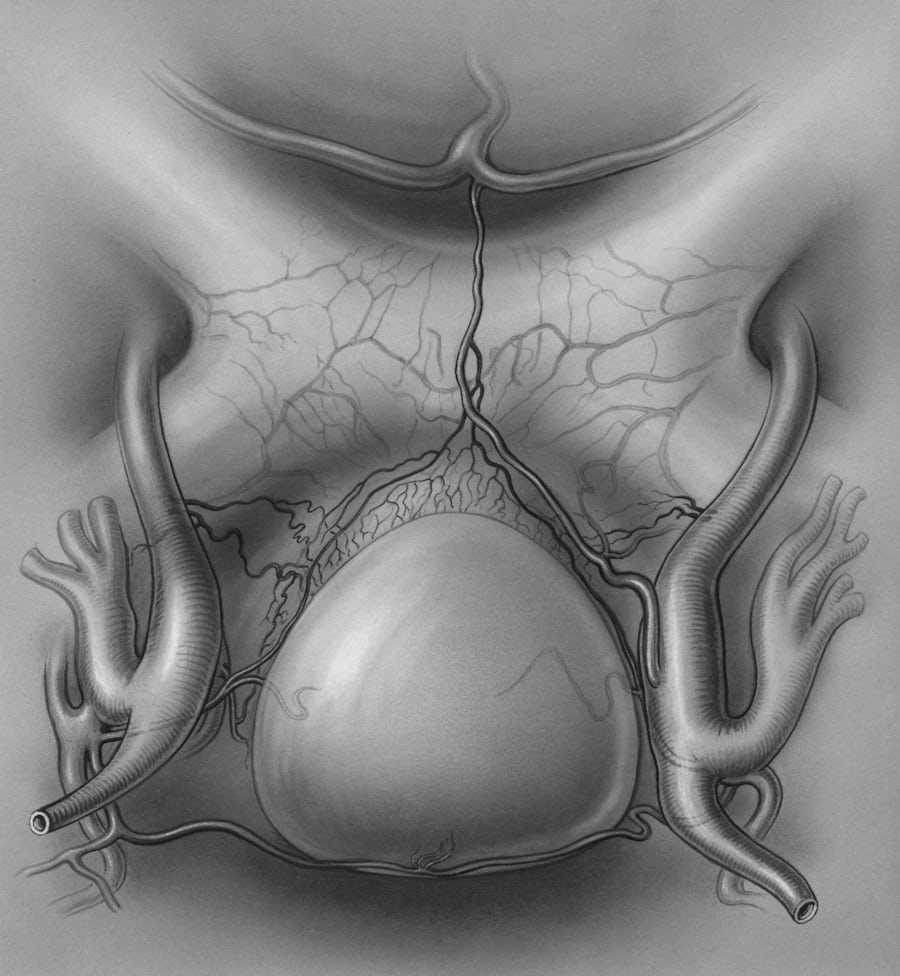
BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, a common condition in aging men. The enlarged prostate can squeeze the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder, leading to bothersome urinary symptoms such as a frequent or urgent need to urinate, a weak urine stream, difficulty starting urination, and the sensation of incomplete bladder emptying.
The primary goal of BPH treatment is to alleviate these symptoms and improve quality of life. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms, the size of the prostate, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences.
Watchful Waiting and Lifestyle Modifications
For men with mild symptoms that do not significantly impact their daily lives, a “watchful waiting” or “active surveillance” approach may be recommended. This involves regular monitoring of symptoms by a healthcare provider without immediate medical intervention.
In conjunction with watchful waiting, or as a first step for many men, lifestyle modifications can provide significant relief:
Fluid Management: Limiting fluid intake, especially in the evening before bedtime, can reduce the need for nighttime urination (nocturia). It is also advisable to reduce the consumption of bladder irritants such as caffeine and alcohol.
Dietary Changes: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, while limiting red meat and processed foods, may be beneficial. Some studies suggest that foods high in zinc, like nuts and legumes, and those containing lycopene, such as tomatoes, can support prostate health.
Regular Exercise: Physical activity, including moderate-intensity exercises like walking, can help manage BPH symptoms. Pelvic floor exercises, also known as Kegels, can strengthen the muscles that control urination.
Bladder Training: This involves urinating at scheduled times to help retrain the bladder and increase its capacity.Double voiding—urinating and then trying to urinate again a few moments later—can help ensure the bladder is fully emptied.
Medications
For men with mild to moderate symptoms, medication is often the next step. Several classes of drugs are effective in treating BPH:
Alpha-Blockers: These medications work by relaxing the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, making it easier to urinate. They provide relatively rapid symptom relief. Common examples include tamsulosin, alfuzosin, doxazosin, and terazosin. Side effects may include dizziness, headache, and retrograde ejaculation (semen entering the bladder instead of being ejaculated).
5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: These drugs, such as finasteride and dutasteride, work by shrinking the prostate gland. They are most effective in men with significantly enlarged prostates. It may take several months to see the full benefits of these medications. Potential side effects include decreased libido and erectile dysfunction.
Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) Inhibitors: While primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction, daily low-dose tadalafil has also been approved for the treatment of BPH symptoms. It works by relaxing the smooth muscles in the bladder and prostate.
Combination Therapy: In some cases, a combination of an alpha-blocker and a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor may be prescribed to provide both rapid symptom relief and long-term prostate shrinkage.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Therapies
For men with moderate to severe symptoms, or for those who do not respond to or cannot tolerate medications, minimally invasive surgical therapies offer a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery with a quicker recovery time. These procedures are typically performed on an outpatient basis.
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): Long considered the gold standard for BPH surgery, TURP involves removing excess prostate tissue using an electrified wire loop inserted through the urethra. It is highly effective but carries risks such as bleeding, infection, and retrograde ejaculation.
Laser Therapies:
GreenLight™ Laser Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate (PVP): This procedure uses a high-powered laser to vaporize and remove obstructive prostate tissue. It generally results in less bleeding and a shorter catheterization time compared to TURP.
Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP): HoLEP uses a laser to remove the entire inner portion of the prostate, which is then morcellated and suctioned out. It is effective for very large prostates and has a low retreatment rate.
UroLift® System: This procedure involves placing small implants to lift and hold the enlarged prostate tissue away from the urethra, opening the urinary channel. It is a good option for men who wish to preserve ejaculatory function.
Rezum™ Water Vapor Therapy: This treatment uses steam to destroy excess prostate tissue. The steam is injected into the prostate, causing the targeted cells to die and be naturally absorbed by the body over time.
Conventional Surgery
In cases of a very large prostate or when other treatments are not suitable, conventional open surgery may be necessary.
Open Prostatectomy: This involves making an incision in the lower abdomen to remove the inner part of the prostate. It is the most invasive option and is reserved for men with a significantly enlarged prostate or those with complications such as bladder stones or bladder damage.
The decision on the most appropriate medical treatment for BPH is a collaborative one between the patient and their urologist. A thorough evaluation, including a discussion of symptoms, a physical examination, and potentially further diagnostic tests, will help determine the best course of action to alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life.